When a current-carrying coil is placed in a magnetic field, there is force acting on the coil. In fact, an induced e.m.f or electromotive force is produced in a conductor which experiences a change of the magnetic field. An induced current flows through the conductor if it is connected in a closed circuit. This phenomenon is called electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electrical potential difference (or voltage) or an induced e.m.f. in a conductor or across a conductor situated in a changing magnetic flux or when there is a change in magnetic flux linked with the conductor.
Concept of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday’s Law state that the strength of the induced e.m.f is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux.
Faraday's Magnetic Field Induction Experiment
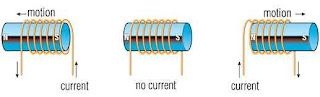
When Michael Faraday made his discovery of electromagnetic induction in 1831, he hypothesized that a changing magnetic field is necessary to induce a current in a nearby circuit. To test his hypothesis he made a coil by wrapping a paper cylinder with wire. He connected the coil to a galvanometer, and then moved a magnet back and forth inside the cylinder. When you move the magnet back and forth, notice that the galvanometer needle moves, indicating that a current is induced in the coil. Notice also that the needle immediately returns to zero when the magnet is not moving. Faraday confirmed that a moving magnetic field is necessary in order for electromagnetic induction to occur.
In this picture an ammeter is connected in the circuit of a conducting loop. When the bar magnet is moved closer to, or farther from the loop, an electromotive force (e.m.f) is induced in the loop. The ammeter indicates currents in different directions depending on the relative motion of magnet and loop. Notice that, when the magnet stops moving, the current returns to zero as indicated by the ammeter.
Lenz’s Law
The direction of the induced current is determined by Lenz’s Law which states that the induced current always flows in the direction in such a way that it opposes the change that produces it.
HEALTH AND LIFESTYLE